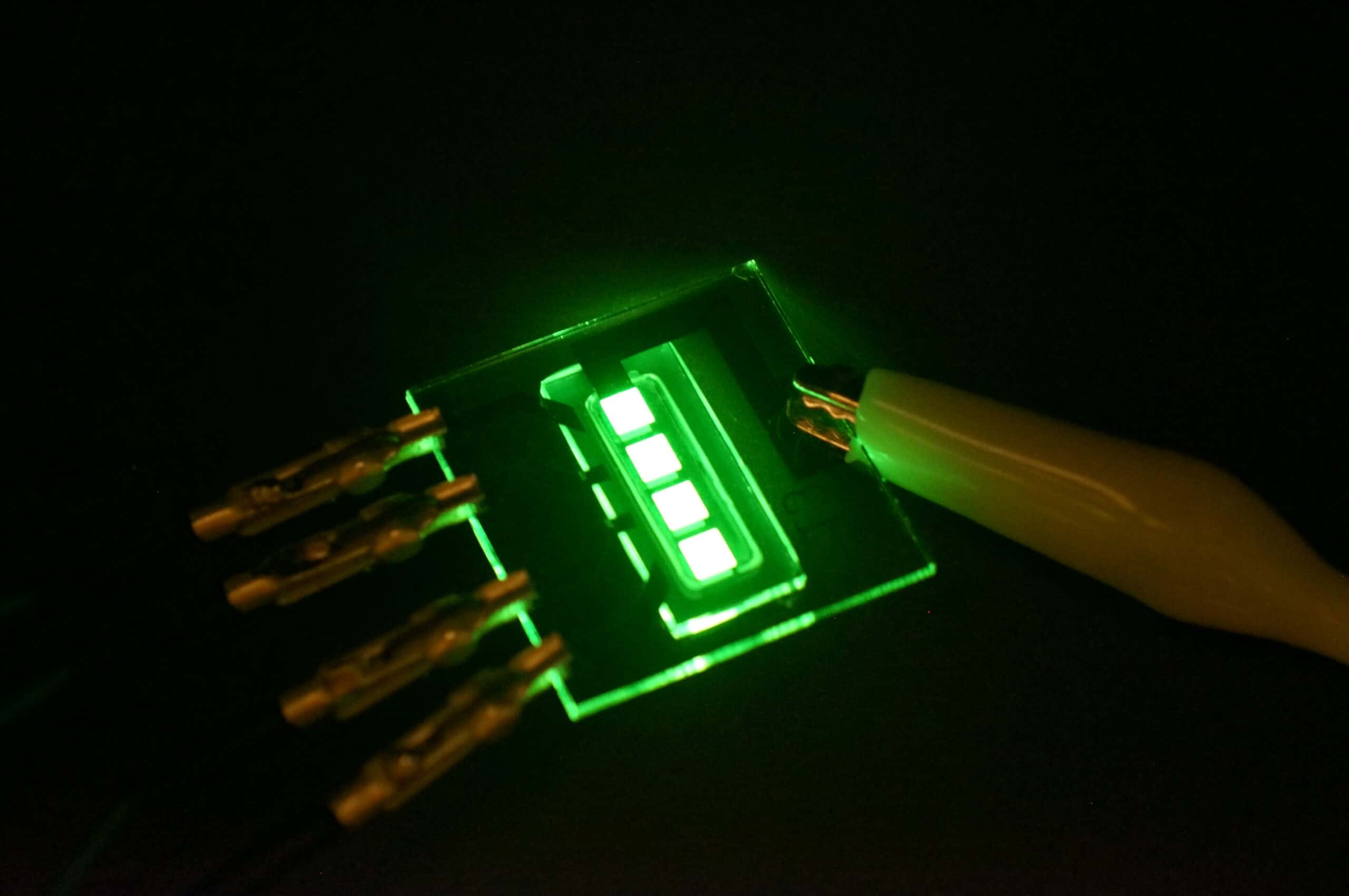
Organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) are ultra-thin and highly efficient light sources. This powerful technology is used in modern display and lighting applications. OLED displays are the new standard in high-end smartphones and are on track to replace LCD technology in tablets, televisions and laptops as well. About 500 million OLED smartphone displays were sold in 2020. OLED displays have high contrast, vibrant colors and can be flexible or semi-transparent. Initial applications for OLED lighting are in the automotive industry and in high-end designer lamps.
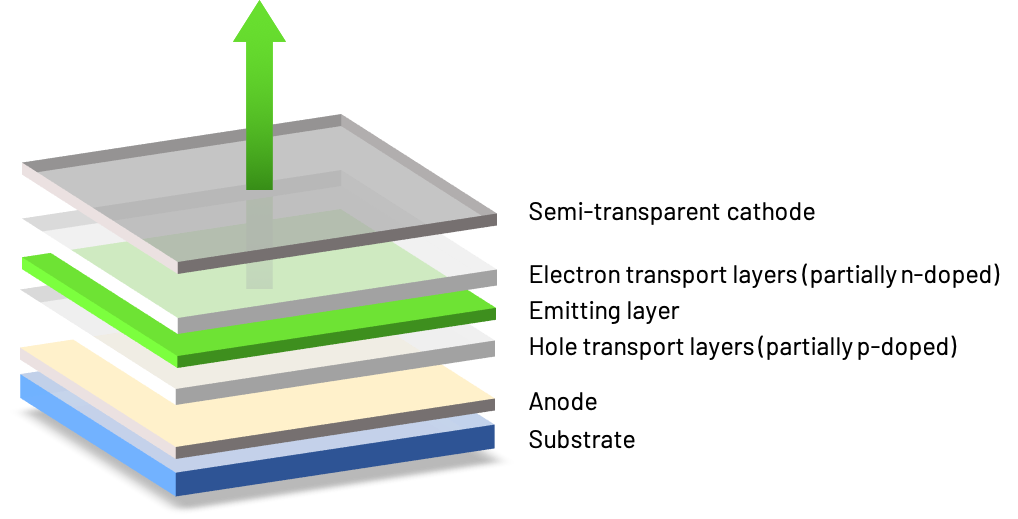
OLEDs consist of a stack of organic semiconducting thin films deposited by thermal vapor deposition in a vacuum onto large glass plates or foils. Printing is an alternative technique with great potential for low-cost production, but there are still some obstacles to overcome. Each layer has its own function. The outer layers are responsible for charge transport to the center of the OLED, where emitter molecules convert electrons and holes (defective electrons) into light. A p-i-n architecture with p- and n-doped charge transport layers and an intrinsic (i) emitting layer has been shown to improve the electrical and optical performance of the device and is therefore used in the vast majority of OLEDs, including smartphone displays. CREDOXYS is developing dopants and transport materials for the p-i-n approach that help make OLEDs more efficient and durable.